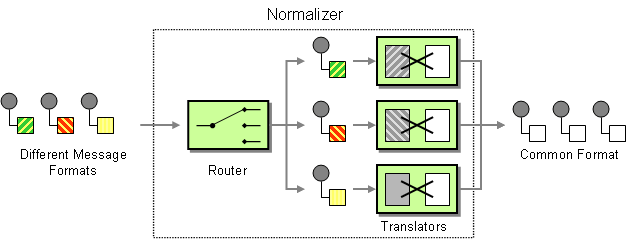
The normalizer pattern is used to process messages that are semantically equivalent, but arrive in different formats. The normalizer transforms the incoming messages into a common format.
In Fuse Mediation Router, you can implement the normalizer pattern by combining a content-based router, which detects the incoming message's format, with a collection of different message translators, which transform the different incoming formats into a common format.
This example shows a Message Normalizer that converts two types of XML messages into a common format. Messages in this common format are then filtered.
Using the Fluent Builders
// we need to normalize two types of incoming messages
from("direct:start")
.choice()
.when().xpath("/employee").to("bean:normalizer?method=employeeToPerson")
.when().xpath("/customer").to("bean:normalizer?method=customerToPerson")
.end()
.to("mock:result");In this case we're using a Java bean as the normalizer. The class looks like this
// Java
public class MyNormalizer {
public void employeeToPerson(Exchange exchange, @XPath("/employee/name/text()") String name) {
exchange.getOut().setBody(createPerson(name));
}
public void customerToPerson(Exchange exchange, @XPath("/customer/@name") String name) {
exchange.getOut().setBody(createPerson(name));
}
private String createPerson(String name) {
return "<person name=\"" + name + "\"/>";
}
} The same example in the XML DSL
<camelContext xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring">
<route>
<from uri="direct:start"/>
<choice>
<when>
<xpath>/employee</xpath>
<to uri="bean:normalizer?method=employeeToPerson"/>
</when>
<when>
<xpath>/customer</xpath>
<to uri="bean:normalizer?method=customerToPerson"/>
</when>
</choice>
<to uri="mock:result"/>
</route>
</camelContext>
<bean id="normalizer" class="org.apache.camel.processor.MyNormalizer"/>