Cloud Foundry Components
Page last updated: October 23, 2015
Cloud Foundry components include a self-service application execution engine, an automation engine for application deployment and lifecycle management, and a scriptable command line interface (CLI), as well as integration with development tools to ease deployment processes. Cloud Foundry has an open architecture that includes a buildpack mechanism for adding frameworks, an application services interface, and a cloud provider interface.
Refer to the descriptions below for more information about Cloud Foundry components. Some descriptions include links to more detailed documentation.
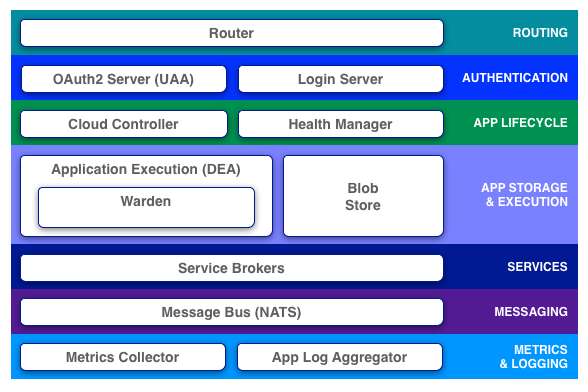
Router
The router routes incoming traffic to the appropriate component, usually the Cloud Controller or a running application on a DEA node.
OAuth2 Server (UAA) and Login Server
The OAuth2 server (the UAA) and Login Server work together to provide identity management.
Cloud Controller
The Cloud Controller is responsible for managing the lifecycle of applications. When a developer pushes an application to Cloud Foundry, she is targeting the Cloud Controller. The Cloud Controller then stores the raw application bits, creates a record to track the application metadata, and directs a DEA node to stage and run the application. The Cloud Controller also maintains records of orgs, spaces, services, service instances, user roles, and more.
Health Manager (HM9000)
HM9000 has four core responsibilities:
- Monitor applications to determine their state (e.g. running, stopped, crashed, etc.), version, and number of instances. HM9000 updates the actual state of an application based on heartbeats and
droplet.exitedmessages issued by the DEA running the application. - Determine applications’ expected state, version, and number of instances. HM9000 obtains the desired state of an application from a dump of the Cloud Controller database.
- Reconcile the actual state of applications with their expected state. For instance, if fewer than expected instances are running, HM9000 will instruct the Cloud Controller to start the appropriate number of instances.
- Direct Cloud Controller to take action to correct any discrepancies in the state of applications.
HM9000 is essential to ensuring that apps running on Cloud Foundry remain available. HM9000 restarts applications whenever the DEA running an app shuts down for any reason, when Warden kills the app because it violated a quota, or when the application process exits with a non-zero exit code.
Refer to the HM9000 readme for more information about the HM9000 architecture.
Application Execution (DEA)
The Droplet Execution Agent manages application instances, tracks started instances, and broadcasts state messages.
Application instances live inside Warden containers. Containerization ensures that application instances run in isolation, get their fair share of resources, and are protected from noisy neighbors.
Blob Store
The blob store holds:
- Application code
- Buildpacks
- Droplets
Service Brokers
Applications typically depend on services such as databases or third-party SaaS providers. When a developer provisions and binds a service to an application, the service broker for that service is responsible for providing the service instance.
Message Bus (NATS)
Cloud Foundry uses NATS, a lightweight publish-subscribe and distributed queueing messaging system, for internal communication between components.
Metrics Collector and App Log Aggregator: Logging and Statistics
The metrics collector gather metrics from the components. Operators can use this information to monitor an instance of Cloud Foundry.
The application log aggregator streams application logs to developers.