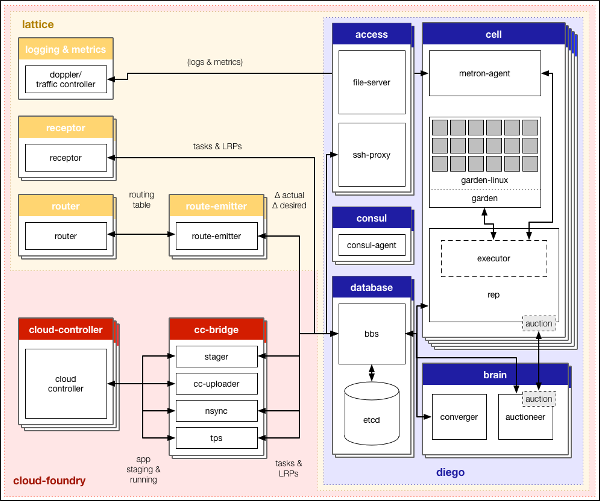
Diego Components
Page last updated: October 21, 2015
This topic describes the components that make up the Diego container management system for Cloud Foundry (CF).
For an overview of the high-level structure of Diego, see the Diego Architecture topic.
The diagram below illustrates the primary Diego components and how they interact with other Cloud Foundry components.
This table describes the major areas in the image above:
| Diagram Color | Scope of Responsibility | Source Code Location | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blue | Running and monitoring Tasks and Long Running Processes (LRPs) | Diego Release | |
| Red | Translating app-specific messages from the Cloud Controller to the Bulletin Board System (BBS) | Stager CC-Uploader Nsync TPS | |
| Yellow | Supporting streaming logs and routing to containers managed by Diego | Diego Release and CF-Release | The Lattice open source project distribution includes these components and offers developers an environment for interacting with Diego. |
Diego Core Components
Components in the Diego core run and monitor Tasks and Long Running Processes (LRPs). The core consists of the following major areas:
Diego Brain
Diego Brain components distribute Tasks and LRPs to Diego Cells, and correct discrepancies between ActualLRP and DesiredLRP counts to ensure fault-tolerance and long-term consistency. The Diego Brain consists of the Auctioneer and the Converger.
Auctioneer
Uses the auction package to run Diego Auctions for Tasks and LRPs
Communicates with Cell Reps over HTTP
Maintains a lock in the BBS that restricts auctions to one Auctioneer at a time
Refer to the Auctioneer repo on GitHub for more information.
Converger
Uses converge methods from the Runtime Schema to analyze snapshots from the BBS to ensure consistency and fault tolerance for Tasks and LRPs
Acts to keep
DesiredLRPcount andActualLRPcount synchronized in the following ways:- If the
DesiredLRPcount exceeds theActualLRPcount, the Converger requests a start auction from the Auctioneer - If the
ActualLRPcount exceeds theDesiredLRPcount, the Converger sends a stop message to the Rep on the Cell hosting an instance
- If the
Monitors for potentially missed messages, resending them if necessary
Maintains a lock in the BBS that limits converge methods to one Converger at a time
Refer to the Converger repo on GitHub for more information.
Diego Cell Components
Diego Cell components manage and maintain Tasks and LRPs.
Rep
Represents a Cell in Diego Auctions for Tasks and LRPs
Mediates all communication between the Cell and the BBS
Ensures synchronization between the set of Tasks and LRPs in the BBS with the containers present on the Cell
Maintains the presence of the Cell in the BBS
Runs Tasks and LRPs by asking the in-process Executor to create a container and
RunActionrecipes
Refer to the Rep repo on GitHub for more information.
Executor
Runs as a logical process inside the Rep
Implements the generic Executor actions detailed in the API documentation
Streams
STDOUTandSTDERRto the Metron agent running on the Cell
Refer to the Executor repo on GitHub for more information.
Garden
Provides a platform-independent server and clients to manage Garden containers
Defines the garden-linux interface for container implementation
Refer to the Garden repo on GitHub for more information.
Metron Agent
Forwards application logs, errors, and application and Diego metrics to the Loggregator Doppler component
Refer to the Metron repo on GitHub for more information.
Database VMs
Diego Bulletin Board System
Maintains a real-time representation of the state of the Diego cluster, including all desired LRPs, running LRP instances, and in-flight Tasks
Provides an RPC-style API over HTTP to Diego Core components and external clients, including the SSH Proxy, CC-Bridge, and Route Emitter.
Refer to the Bulletin Board System repo on GitHub for more information.
etcd
- Provides a consistent key-value data store to Diego
Access VMs
File Server
- Serves static assets used by various Diego components, particularly the App Lifecycle binaries
Refer to the File Server repo on GitHub for more information.
SSH Proxy
- Brokers connections between SSH clients and SSH servers running inside instance containers
Refer to the Diego SSH repo on GitHub for more information.
Consul
Provides dynamic service registration and load balancing through DNS resolution
Provides a consistent key-value store for maintenance of distributed locks and component presence
Refer to the Consul repo on GitHub for more information.
Consuladapter
Consuladapter provides a driver for interfacing with etcd.
Refer to the Consuladapter repo on GitHub for more information.
Cloud Controller Bridge Components
The Cloud Controller Bridge (CC-Bridge) components translate app-specific requests from the Cloud Controller to the BBS. These components include the following:
Stager
Translates staging requests from the Cloud Controller into generic Tasks and LRPs
Sends a response to the Cloud Controller when a Task completes
Refer to the Stager repo on GitHub for more information.
CC-Uploader
Mediates uploads from the Executor to the Cloud Controller
Translates simple HTTP POST requests from the Executor into complex multipart-form uploads for the Cloud Controller
Refer to the CC-Uploader repo on GitHub for more information.
Nsync
Listens for app requests to update the
DesiredLRPscount and updatesDesiredLRPsthrough the BBSPeriodically polls the Cloud Controller for each app to ensure that Diego maintains accurate
DesiredLRPscounts
Refer to the Nsync repo on GitHub for more information.
TPS
Provides the Cloud Controller with information about currently running LRPs to respond to
cf appsandcf app APP_NAMErequestsMonitors
ActualLRPactivity for crashes and reports them the Cloud Controller
Refer to the TPS repo on GitHub for more information.
Platform-specific Components
Garden Backends
Garden contains a set of interfaces that each platform-specific backend must implement. These interfaces contain methods to perform the following actions:
- Create and delete containers
- Apply resource limits to containers
- Open and attach network ports to containers
- Copy files into and out of containers
- Run processes within containers
- Stream
STDOUTandSTDERRdata out of containers - Annotate containers with arbitrary metadata
- Snapshot containers for redeploys without downtime
Refer to the Garden repo on GitHub for more information.
Current Implementations
- Garden-Linux provides a Linux-specific implementation of a Garden interface.
App Lifecycles
App Lifecycles implement deployment strategies. Each App Lifecycle contains the following three binaries:
The Builder, which stages a CF application. The CC-Bridge runs the Builder as a Task on every staging request. The Builder performs static analysis on the application code and does any necessary pre-processing before the application is first run.
The Launcher, which runs a CF application. The CC-Bridge sets the Launcher as the Action on the
DesiredLRPfor the application. The Launcher executes the start command with the correct system context, including working directory and environment variables.The Healthcheck, which performs a status check on running CF application from inside the container. The CC-Bridge sets the Healthcheck as the Monitor action on the
DesiredLRPfor the application.
Current Implementations
Buildpack App Lifecycle implements the Cloud Foundry buildpack-based deployment strategy.
Docker App Lifecycle implements a Docker deployment strategy.
Other Components
Route-Emitter
Monitors
DesiredLRPandActualLRPstates, emitting route registration and unregistration messages to the Cloud Foundry router when it detects changesPeriodically emits the entire routing table to the Cloud Foundry router
Refer to the Route-Emitter repo on GitHub for more information.