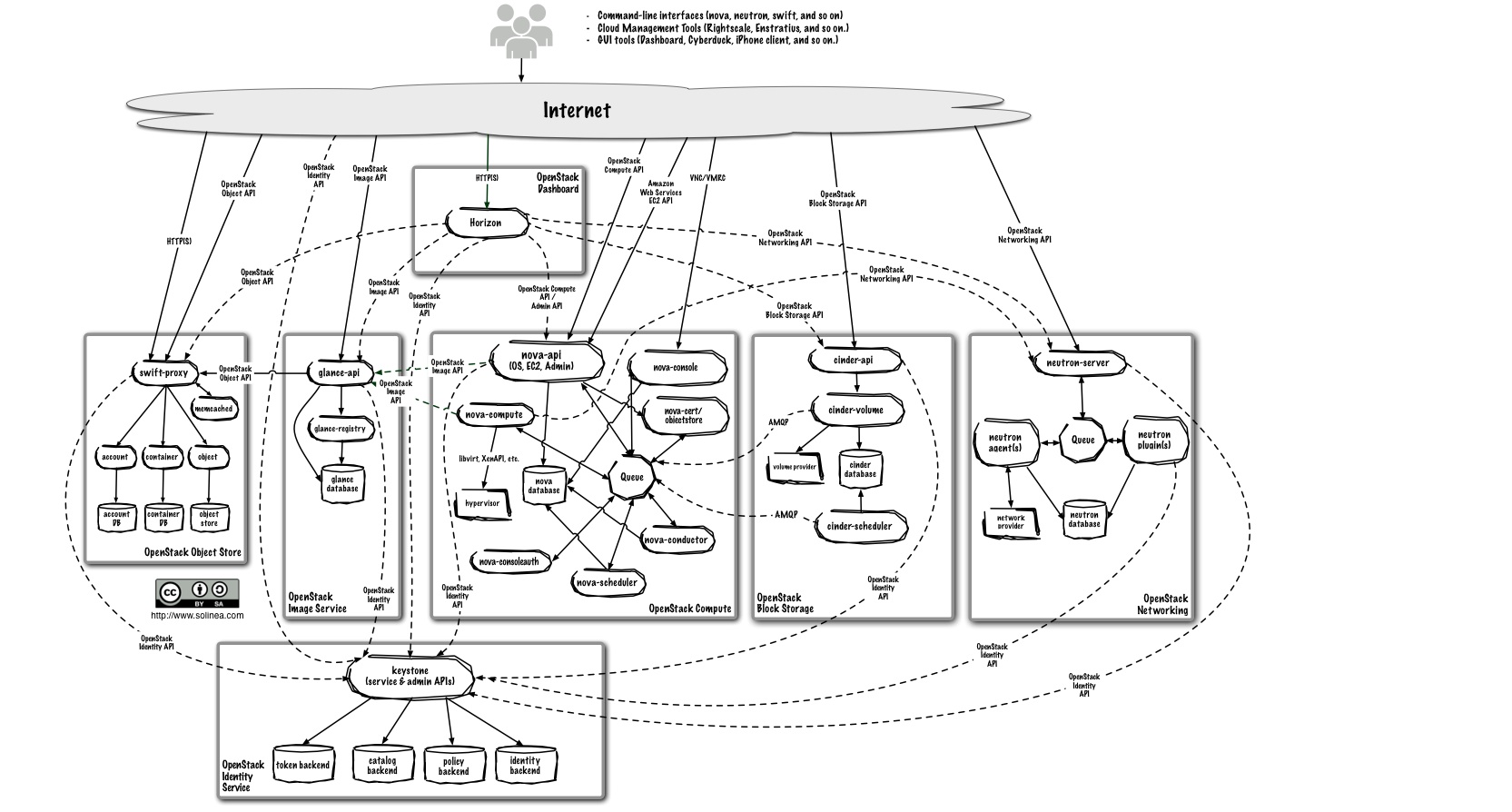
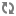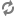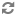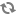To design, deploy, and configure OpenStack, administrators must understand the logical architecture.
OpenStack modules are one of the following types:
- Daemon
Runs as a background process. On Linux platforms, a daemon is usually installed as a service.
- Script
Installs a virtual environment and runs tests. For example, the
run_tests.shscript installs a virtual environment and runs unit tests on a service.- Command-line interface (CLI)
Enables users to submit API calls to OpenStack services through easy-to-use commands.
The following diagram shows the most common, but not the only, architecture for an OpenStack cloud:
As in Figure 1.1, “OpenStack conceptual architecture”, end users can interact through the dashboard, CLIs, and APIs. All services authenticate through a common Identity Service and individual services interact with each other through public APIs, except where privileged administrator commands are necessary.