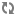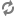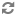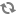The Compute service uses dnsmasq as the DHCP server when running with
either that Flat DHCP Network Manager or the VLAN Network
Manager. The nova-network service is responsible for
starting up dnsmasq processes.
The behavior of dnsmasq can be customized by creating a
dnsmasq configuration file. Specify the config file using
the dnsmasq_config_file configuration
option. For
example:
dnsmasq_config_file=/etc/dnsmasq-nova.conf
See the high availability section for an example of how to change the behavior of dnsmasq using a dnsmasq configuration file. The dnsmasq documentation has a more comprehensive dnsmasq configuration file example.
Dnsmasq also acts as a caching DNS server for instances.
You can explicitly specify the DNS server that dnsmasq
should use by setting the dns_server
configuration option in
/etc/nova/nova.conf. The
following example would configure dnsmasq to use Google's
public DNS
server:
dns_server=8.8.8.8
Dnsmasq logging output goes to the syslog (typically
/var/log/syslog or
/var/log/messages, depending on
Linux distribution). The dnsmasq logging output can be
useful for troubleshooting if VM instances boot
successfully but are not reachable over the
network.
A network administrator can run nova-manage fixed
reserve
--address= to
specify the starting point IP address (x.x.x.x) to reserve
with the DHCP server. This reservation only affects which
IP address the VMs start at, not the fixed IP addresses
that the nova-network service places on the bridges.x.x.x.x