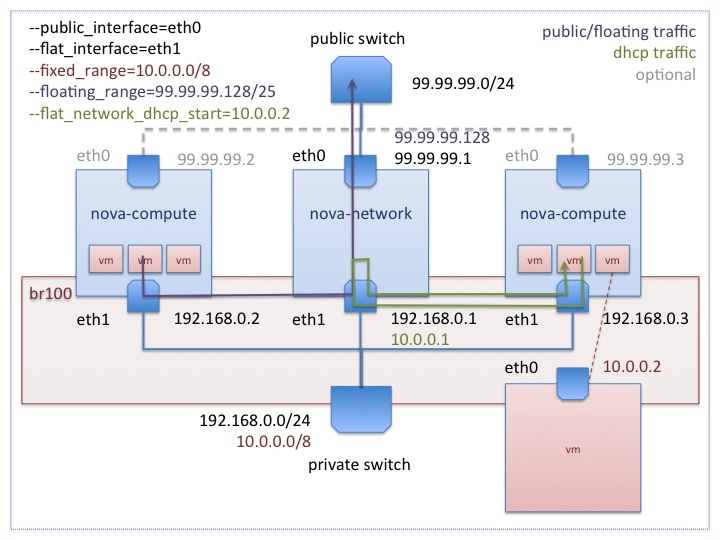
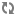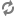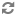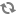When using the libvirt driver, the setup will look like the figure below:
Be careful when setting up
--flat_interface. If you
specify an interface that already has an IP it will
break and if this is the interface you are connecting
through with SSH, you cannot fix it unless you have
ipmi/console access. In FlatDHCP mode, the setting for
--network_size should be number
of IPs in the entire fixed range. If you are doing a
/12 in CIDR notation, then this number would be 2^20
or 1,048,576 IP addresses. That said, it will take a
very long time for you to create your initial network,
as an entry for each IP will be created in the
database.
If you have an unused interface on your hosts (eg
eth2) that has connectivity with no IP address,
you can simply tell FlatDHCP to bridge into the
interface by specifying
flat_interface=
in your configuration file. The network host will
automatically add the gateway ip to this bridge.
If this is the case for you, edit your
<interface>nova.conf file to contain
the following lines:
dhcpbridge_flagfile=/etc/nova/nova.conf
dhcpbridge=/usr/bin/nova-dhcpbridge
network_manager=nova.network.manager.FlatDHCPManager
fixed_range=''
flat_network_bridge=br100
flat_interface=eth2
flat_injected=False
public_interface=eth0
You can also add the unused interface to br100 manually and not set flat_interface.
Integrate your network interfaces to match this configuration.