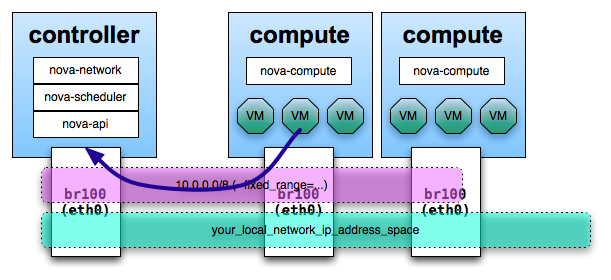
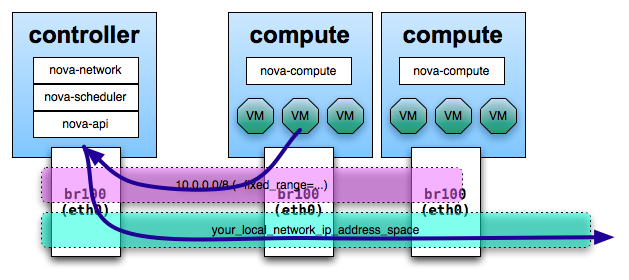
In any set up with FlatNetworking, the host with
nova-network on it is responsible for forwarding
traffic from the private network dynamically
determined by Compute with the
fixed_range='' directive in
nova.conf. This host needs to
have a bridge interface (e.g.,
br100) configured and talking
to any other nodes that are hosting VMs. With either
of the Flat Networking options, the default gateway
for the virtual machines is set to the host which is
running nova-network.
When a virtual machine sends traffic out to the public networks, it sends it first to its default gateway, which is where nova-network is configured.
Next, the host on which nova-network is configured acts as a router and forwards the traffic out to the Internet.
![[Warning]](../common/images/admon/warning.png) | Warning |
|---|---|
If you're using a single interface, then that interface (often eth0) needs to be set into promiscuous mode for the forwarding to happen correctly. This does not appear to be needed if you're running with physical hosts that have and use two interfaces. |